Feature selection is central to contemporary high-dimensional data analysis. Group structure among features arises naturally in various scientific problems. Many methods have been proposed to incorporate the group structure information into feature selection. However, these methods are normally restricted to a linear regression setting. To relax the linear constraint, we design a new Deep Neural Network (DNN) architecture and integrating it with the recently proposed knockoff technique to perform nonlinear group-feature selection with controlled group-wise False Discovery Rate (gFDR).
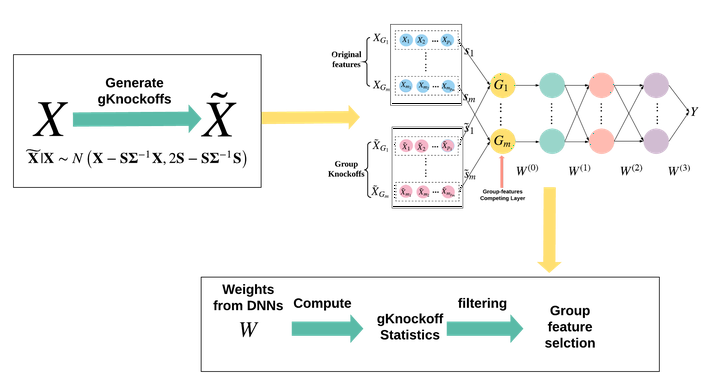
Procedure
- Generating group knockoff features;
- Incorporating original features and group knockoff features into a designed DNN architecture. The DNN structure is built upon an MLP with the major distinction that it has a plugin Group-feature Competing Layer.
- Computing knockoff statistics and filtering out the unimportant groups.
Contribution
- End-to-end group-wise feature selection and deep representations.
- Learned neural networks with enhanced interpretability and reproducibility.
- More computationally feasible neural network.
- Superior performance in terms of power and controlled gFDR in both linear and nonlinear settings for high-dimensional synthetic and real world genome-wide association studies in the $p\gg n$ regime.
- Comprehensive experimental results to characterize the performance of our approach with varying key parameters, model architecture changes and robustness to model misspecification.